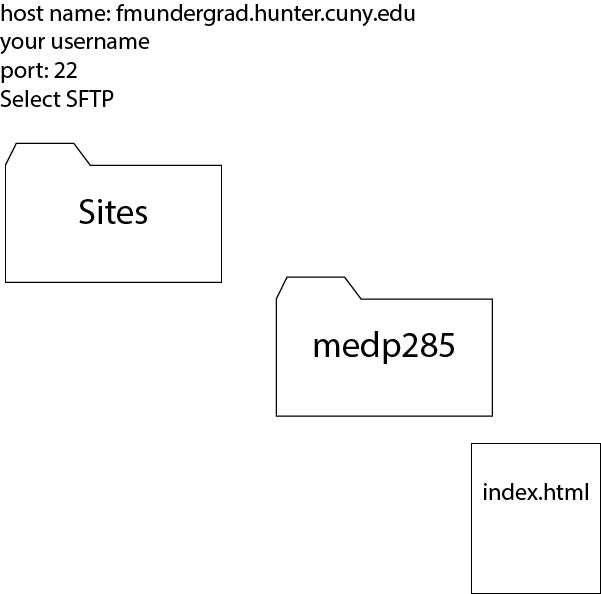
Process
1. Start simple, figure out and organize your content.
2. Draw a flow chart of how you want people to encounter the content and how to organize it via a menu or navigation bar.
3. Create a wireframe for each page that varies in the site or section on a single page site. The wireframe does not include content or design, it's merely the general layout of a page.
4. Sketch out a layout that may be used as a template.
Process
5. Use HTML and CSS that you understand to markup and design your layout.
6. Once you have a basic working site, begin to add the various libraries and coded elements. Do so one at a time and save different versions as you go. Doing it step by step (starting with jQuery) will allow you to see where things may break...
| HTML | CSS | JavaScript | PHP/Python/Ruby... | MySQL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Design | Behavior | Brains | Storage |
| Client-side, browser organizes markup | Client-side, browser visualizes design | Client-side, browser interprets commands | Server-side, server interprets commands | Server-side, queries data |
| Hyper Text Markup Language describes the various components of a web document. | Cascading Style Sheets stylize the elements in a web document. | JavaScript adds interactivity and behaviors to a web document. | PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor manages application logic and handles form processing. | MySQL: Structured Query Langauge is a relational database used to store information for web applications |
Software
Tools to Know
- Text Editor i.e. Atom, Text Wragnler, Sublime...
- Use of FTP
- Basic to Advanced Photoshop and/or Illustrator
Web Extensions
File Naming & Extensions
- File Types & Naming Conventions
begin with lower case alphabetical character; no spaces; end with extension:pageOne.html or page_one.html or page01.html
- HTML - extension: .html
- CSS - extension: .css
- Basic JS or Use of Frameworks - extension: .js
- Navigating a Server
HTML
<element>Content</element>
- open and close tags for all markup elements
- properly nested tags
- use only lower case
<br> <hr>
Empty tags do not require a closing tags.
HTML
Block elements - h1, h2..., div, p, ol, ul, pre, address, blockquote, form, table
Block level elements always start on a new line and take up the full width available.
Inline elements - strong, span, em, img
Inline elements do not start a new line and only take up as much width as necessary.
HTML
attributes -
<img src="photo.jpg" alt="landscape">
comments -
<!-- My comment -->
HTML - DOM
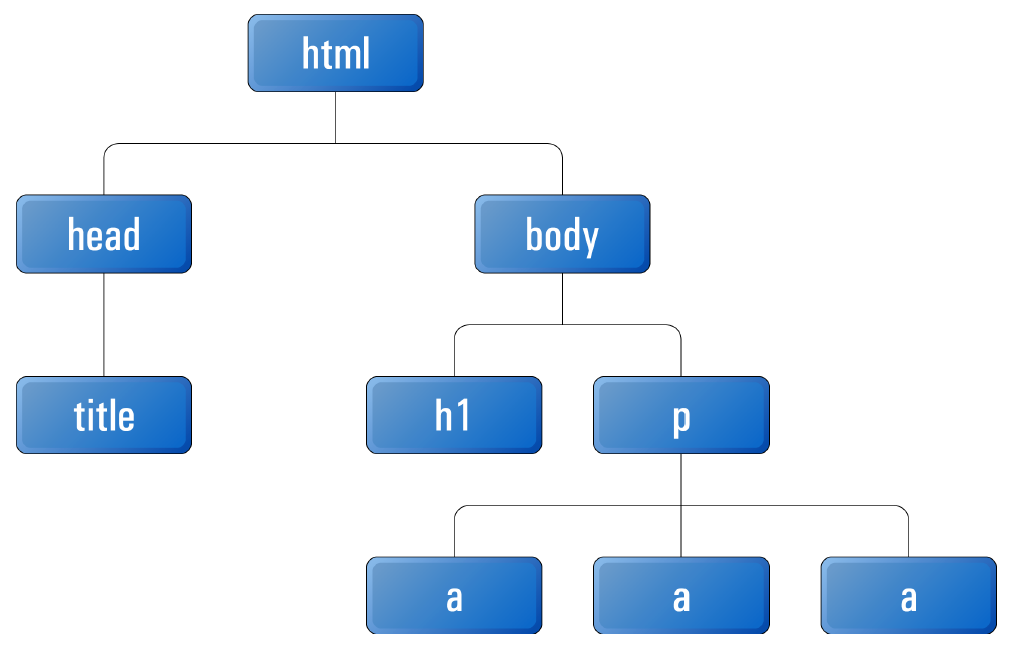
HTML Review - Lists - ul, ol, li
Lists are very popular
<ul> <li>Item 1</li> <li>Item 2</li> </ul>
HTML - hyperlink, table, forms
Anchor tag - a
<a href="link.html">Link</a>
<a href="http://www.link.html" target="_blank">Link</a>
Assemble a table for tabulated data, NOT DESIGN
Forms - a primary means of information submission.
HTML - HTML5
Key syntax features of HTML5 include <video>, <audio> and <canvas> elements, as well as the integration of scalable vector graphics (SVG) content. These features are designed to more easily include multimedia and graphic content without the use of plugins.
Stable HTML5 was released in 2014 and HTML 5.1 2016; we will be using HTML5. However, I will be using the space and forward slash / to close self closing tags or empty tags such as the meta tag or br tag (for break). Javascript libraries such as React require the forward slash to close empty tags.
HTML - Search Engine Optimization
SEO process of improving a websites' ranking in search engines.
- Keywords - think non-specialized, local
- Broad keywords: Short, not specific - "digital graphics, web design"
- Specific keywords: many adjectives or words that make the search very targeted - "animations by William Kentridge"
- Branded keywords: words that are specific to a company or brand
HTML - meta tag
Use of meta tag to identify a page
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta name="title" lang="en" content="Project Title">
<meta name="creator" lang="en" content="Your Name">
<meta name="subject" lang="en" content="Topic">
<meta name="description" lang="en" content="Description.">
<meta name="keywords" content="keyword 1, keyword 2">
<meta name="viewport" content="user-scalable=no, width=device-width">
</head>
HTML - Open Graph (og) Protocol
Use og meta tags to inform social media links to your site (introduced by FB 2010). Og property/value may be added to general meta tags.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta property="og:title" name="title" lang="en" content="Project Title">
<meta property="og:url" content="http://yourURL.com">
</head>
HTML - favicon.ico - Branding
The "favicon" is used to add a 16x16 pixel icon that appears in the title bar of your page and is saved as the page icon when visitors save a page to the favorite list or bookmark. Add the link tag for the favicon within the head tags. Web pages may also be saved to mobile screens, if the correct dimensions are available from a page with the correct link, that icon is saved to the screen. Favicon.ico & App Icon Generator makes resizing and markup easy.
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="favicon.ico">
HTML - SEO
Page Rank
Google page rank determines your website's authority by the number of other websites that link to your website.
Check ranking:
Page Ranking Checker
The best way to increase your page rank is for other "popular" websites to link to your website, and here is a detalied explanation of how page rank work and why it still matters.
HTML - SEO
Page Rank
Search engines pay close attention to the <title> tag as they categorize your website. Use this opportunity to think critically about its contents.
Search engines also use heading tags (h1 - h6) to determine what a page is about and what content is most important.
HTML - SEO
Page Rank
Content writers often bold, italicize, or emphasize a few important words in paragraph text to help search engines to determine which keywords are most relevant.
The number of required clicks to get to a page from the homepage. Pages that are available in one click are deemed more important than those that are nearly hidden and require more than 3 clicks to reach.